Automatically logging keras experiments¶
Comet.ml will monitor training, logging metrics, parameters, and histograms to your keras code without requiring you to do anything other than adding these lines of code to your Keras script, and setting the experiment parameters to the appropriate values for what you would like to log:
```python from comet_ml import Experiment experiment = Experiment( auto_metric_logging=True, auto_param_logging=True, auto_histogram_weight_logging=True, auto_histogram_gradient_logging=True, auto_histogram_activation_logging=True, )
Your code here...¶
```
For more information on getting started, see details on the Comet config file.
Keras Auto-logging Controls¶
The Comet Keras auto-logger can automatically log:
- model/graph description
- steps and epochs
- metrics (such as loss and accuracy)
- hyperparameters
- optimizer config
- number of trainable parameters
- histograms for weights and biases
- histograms for activations
- histograms for gradients
Each of these can be controlled through an experiment parameter, environment variable, or a configuration setting:
| Item | Experiment Parameter | Environment Setting | Configuration Setting |
|---|---|---|---|
| model/graph description | log_graph | COMET_AUTO_LOG_GRAPH | comet.auto_log.graph |
| metrics | auto_metric_logging | COMET_AUTO_LOG_METRICS | comet.auto_log.metrics |
| metric logging rate | auto_metric_step_rate | COMET_AUTO_LOG_METRIC_STEP_RATE | comet.auto_log.metric_step_rate |
| hyperparameters | auto_param_logging | COMET_AUTO_LOG_PARAMETERS | comet.auto_log.parameters |
| command-line arguments | parse_args | COMET_AUTO_LOG_CLI_ARGUMENTS | comet.auto_log.cli_arguments |
| weights/biases | auto_histogram_weight_logging | COMET_AUTO_LOG_HISTOGRAM_WEIGHTS | comet.auto_log.histogram_weights |
| gradients | auto_histogram_gradient_logging | COMET_AUTO_LOG_HISTOGRAM_GRADIENTS | comet.auto_log.histogram_gradients |
| activations | auto_histogram_activation_logging | COMET_AUTO_LOG_HISTOGRAM_ACTIVATIONS | comet.auto_log.histogram_activations |
| histogram logging rate | auto_histogram_epoch_rate | COMET_AUTO_LOG_HISTOGRAM_EPOCH_RATE | comet.auto_log.histogram_epoch_rate |
In addition, you can control exactly which inputs at which layers are logged for activations and gradient histogram logging.
Histograms¶
With the keras auto-logger, you can log histograms for:
- weights and biases
- gradients
- activations
These histograms appear on the Histogram Tab in the user interface:
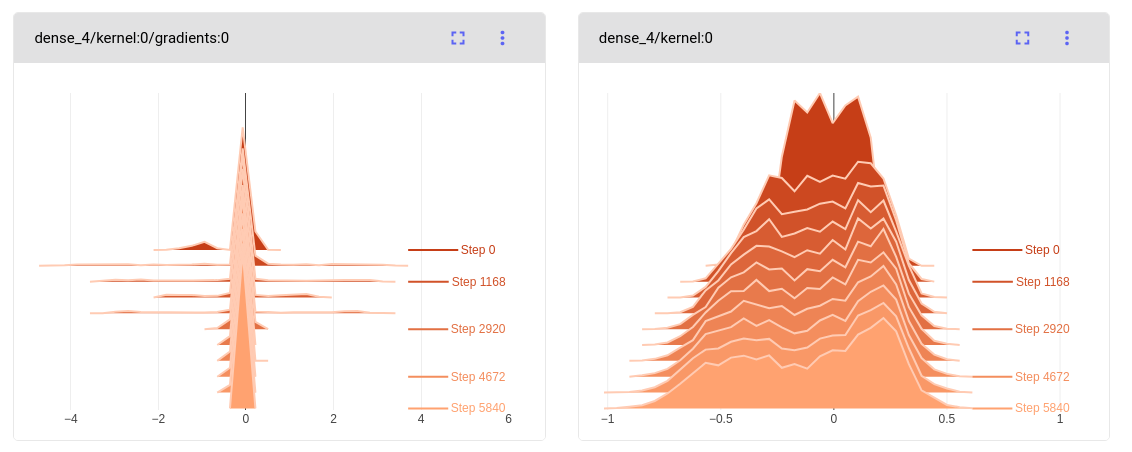
The histograms for weights and biases are logged for all layers before
training, and for every auto_histogram_epoch_rate epochs (default
1).
The histogram activations are logged for the selected inputs/targets
(comet.keras.histogram_activation_index_list with a default of the
first pattern), at the selected layers
(comet.keras.histogram_activation_layer_list with a default of the
last layer).
For activation histograms:
| Item | Configuration Setting |
|---|---|
| which inputs | comet.keras.histogram_activation_index_list |
| which layers | comet.keras.histogram_activation_layer_list |
Info
To auto-log activations, you must be using TensorFlow, version 1.13 or greater. Inputs must be in a tensor or numpy format (e.g., DataSets are not yet supported). Note that logging activations from an input layer does not work with TensorFlow version 1.
The histogram gradients of the weights/biases with respect to the loss
are logged for the selected inputs/targets
(comet.keras.histogram_gradient_index_list with a default of the
first pattern), at the selected layers
(comet.keras.histogram_gradient_layer_list with a default of the
last layer).
For gradient histograms:
| Item | Configuration Setting |
|---|---|
| which inputs | comet.keras.histogram_gradient_index_list |
| which layers | comet.keras.histogram_gradient_layer_list |
Info
To auto-log gradients, you must be using TensorFlow, version 2.2.1 or greater, or Keras 2.4.3 and greater. Inputs and targets must be in a tensor or numpy format (e.g., DataSets are not yet supported).
Each of input of the index lists is composed of an empty string, or a list of index positions. If more than one index is given, separate the values with a comma.
For example, to indicate that you would like to log the activations for the first three input patterns, use:
shell
export COMET_KERAS_HISTOGRAM_ACTIVATION_INDEX_LIST="0,1,2"
Each of layer list is composed of a list of index positions, negative index positions, or layer names. If more than one value is given, separate them with a comma.
For example, to indicate that you would like to log the gradients at the first layer, last layer, and a layer named "hidden", use:
shell
export COMET_KERAS_HISTOGRAM_GRADIENT_LAYER_LIST="0,-1,hidden"
Each of the histograms logged can have a "prefix" attached to the
histogram name in the UI. The prefix is set via the configuration
setting comet.keras.histogram_name_prefix and can be composed of any
of the following components:
| Histogram name prefix component | Meaning |
|---|---|
{model_name} |
Name of the keras model |
{layer_name} |
Name of the keras layer |
{layer_num} |
Number of the keras layer |
{max_digits} |
Number of digits in last keras layer |
By default, the prefix is {layer_num:0{max_digits}d} (using Python's
formatting syntax) which would give prefixes like:
01/input/kernel:0
05/hidden/bias:0
10/output/activation:all
Finally, you can control the following items as well:
| Item | Meaning | Default value |
|---|---|---|
| comet.keras.histogram_batch_size | number of patterns to process at once when logging all | 1000 |
| comet.logging.metrics_ignore | names of metrics to ignore | keras:batch_size,keras:batch_batch |
| comet.logging.parameters_ignore | names of parameters to ignore | keras:verbose,keras:do_validation,keras:validation_steps |
For more details on passing in parameters to the experiment, please see Experiment(). For more details on setting up configuration variables, see Python Configuration.
The Comet.ml Keras callback¶
Comet.ml logs your experiment through a callback executed when you run
model.fit() in Keras. You do not need to add this callback yourself,
we do it for you automatically. However, if you ever need to access
the callback manually, simply call
Experiment.get_keras_callback().
How to report manually¶
You can log additional parameters beyond what Comet.ml automatically collects using Experiment.log_parameter().
```python
from comet_ml import Experiment
create an experiment¶
experiment = Experiment( project_name='mnist', ) from tensorflow import keras batch_size = 128
experiment.log_parameter("batch_size", 128) ```
You can log an entirely customized list of parameters to your experiment by using Experiment.log_parameters().
```python from comet_ml import Experiment from tensorflow.keras.models import Sequential from tensorflow.keras.layers import Dense, Dropout
experiment = Experiment( project_name="my project name", auto_param_logging=False, ) batch_size = 128 num_classes = 10 epochs = 20
params={ "batch_size":batch_size, "epochs":epochs, "num_classes":num_classes}
experiment.log_parameters(params) ```
Context Manager (Train/Test/Validate)¶
You can also log specific metrics to training and test contexts with our context managers Experiment.train(), Experiment.validate() and Experiment.test()
```python from comet_ml import Experiment from tensorflow.keras.models import Sequential from tensorflow.keras.layers import Dense, Dropout
experiment = Experiment( project_name="my project name", auto_param_logging=True, auto_histogram_weight_logging=True, auto_histogram_gradient_logging=True, auto_histogram_activation_logging=True, ) batch_size = 128 num_classes = 10 epochs = 20
params={ "batch_size":batch_size, "epochs":epochs, "num_classes":num_classes}
experiment.log_parameters(params)
define model here¶
with experiment.train(): history = model.fit(x_train, y_train, batch_size=batch_size, epochs=epochs, verbose=1, callbacks=[EarlyStopping(monitor='loss', min_delta=1e-4, patience=3, verbose=1, mode='auto')])
with experiment.test(): loss, accuracy = model.evaluate(x_test, y_test) print(loss, accuracy) metrics = { 'loss':loss, 'accuracy':accuracy } experiment.log_metrics(metrics) ```
End-to-end example¶
Here is a simple end-to-end Keras example which uses a Dense NN on the MNIST dataset.
For more examples using Keras, see our Comet Examples Github repository.
```python from comet_ml import Experiment
create an experiment with your api key¶
experiment = Experiment( project_name='mnist', auto_param_logging=False, auto_histogram_weight_logging=True, auto_histogram_gradient_logging=True, auto_histogram_activation_logging=True, )
from tensorflow import keras from tensorflow.keras.datasets import mnist from tensorflow.keras.models import Sequential from tensorflow.keras.layers import Dense, Dropout from tensorflow.keras.callbacks import EarlyStopping
batch_size = 128 num_classes = 10 epochs = 20 num_nodes = 64 optimizer = 'adam' activation = 'relu'
the data, shuffled and split between train and test sets¶
(x_train, y_train), (x_test, y_test) = mnist.load_data()
x_train = x_train.reshape(60000, 784) x_test = x_test.reshape(10000, 784) x_train = x_train.astype('float32') x_test = x_test.astype('float32') x_train /= 255 x_test /= 255 print(x_train.shape[0], 'train samples') print(x_test.shape[0], 'test samples')
convert class vectors to binary class matrices¶
y_train = keras.utils.to_categorical(y_train, num_classes) y_test = keras.utils.to_categorical(y_test, num_classes)
these will all get logged¶
params={'batch_size':batch_size, 'epochs':epochs, 'layer1_type':'Dense', 'layer1_num_nodes':num_nodes, 'layer1_activation':activation, 'optimizer':optimizer } model = Sequential() model.add(Dense(num_nodes, activation='relu', input_shape=(784,)))
model.add(Dense(256, activation='relu'))¶
model.add(Dense(num_classes, activation='softmax'))
print model.summary() to preserve automatically in Output tab¶
print(model.summary())
model.compile(loss='categorical_crossentropy', optimizer=optimizer, metrics=['accuracy'])
will log metrics with the prefix 'train_'¶
with experiment.train(): history = model.fit(x_train, y_train, batch_size=batch_size, epochs=epochs, verbose=1, validation_data=(x_test, y_test), callbacks=[EarlyStopping(monitor='val_loss', min_delta=1e-4,patience=3, verbose=1, mode='auto')])
will log metrics with the prefix 'test_'¶
with experiment.test(): loss, accuracy = model.evaluate(x_test, y_test) metrics = { 'loss':loss, 'accuracy':accuracy } experiment.log_metrics(metrics)
experiment.log_parameters(params) experiment.log_dataset_hash(x_train) #creates and logs a hash of your data ```
For additional examples, please see: